Google is not just a search engine, it is the technological giant that has been revolutionising technology for decades with its search engine and the development of digital marketing. We are talking about tools such as Google Adwords, Google AdSense, Google Analytics, Google Trends...
Including Google in your digital marketing strategy will help your company to attract users who are looking for something specific. Google ads make it possible for brands to appear right at the moment when people have a need and are actively looking for a way to solve it.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is an advertising service for businesses that want their ads to appear in Google's search results and advertising network.
Let's start at the beginning: Google Ads is the star tool of SEM. Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is "paid" search engine advertising. We can also refer to them as SEA or Search Engine Advertising. And, they are the complete opposite of SEO or Search Engine Optimisation. That is, those actions that contribute to the organic positioning of a brand's content.
In this article we are going to see the basics of Google Ads and how to launch campaigns step by step to make your ads a success. Let's start!
Google Ads Basics
We have put together a glossary of the most common terms you may come across when launching a Google Ads campaign.
-
-
Search term: As its name suggests, terms that users use to make active queries in the Google search engine.
-
-
-
Keyword: Keyword that we bid on and that should respond as closely as possible to the users' search intent.
-
Impressions: Number of times our ad appears in search results or elsewhere on the Google network.
-
Clicks: Number of times that some area of the Google ad is clicked on, taking the user to any of the possible destinations: a web page, a call, a map, a form, etc.
-
CTR: Percentage of impacted users who have clicked on a brand's ads.
-
CPC: The value we will pay for each click users make on an ad.
-
Quality Score: Score that Google gives us as an advertiser based on the keywords we have bought. Depending on this score, our ads will be more or less economical in relation to the competition. The quality score is measured based on 3 essential variables: keywords, ad relevance and landing page experience.
-
A/B testing: Testing two variants of some of the elements of an ad (creativity, copy...) to compare their performance and apply the results.
-
Retargeting: Re-targeting users who have previously interacted online with a brand.
-
Search network: Group of search-related websites where your ads and organic product cards can be displayed.
-
Display network: Group of more than two million websites, videos and apps where your ads can appear.
-
Now that you know the basic Google vocabulary, let's take a look at how Google Ads works.
How does Google Ads work?
Google Ads is all about the type of campaign and the bidding strategy we choose. Depending on both, our ads will be displayed based on one metric or another. For example, if you want to generate traffic to your website, ideally you should prioritise clicks. The Cost Per Click (CPC) bidding strategy could be the right one for your campaign.
To rank well, the most important thing is relevance. But what are the keys for Google to consider us relevant? The relationship between the keywords and the ads we create.
The two parameters that Google will look at to determine how relevant we are:
-
-
CTR (Click Through Rate): This is the indicator par excellence that will determine how we are doing. We look for the percentage of clicks on our ad to be high, ideally above 5%.
-
Quality Score: Based on the expected CTR, ad match and landing page experience, Google will rank us on a keyword. We are looking for a score of more than 7 on a scale of 1 to 10.
-
Therefore, for our Google Ads campaigns to be relevant, it is essential to master the matching of keywords according to the results we want to obtain. There are 5 types of match in Google:
-
Broad match: The ad will appear whenever the user enters that word in their search. We can appear in searches in which we are not relevant. Example: paddle tennis shorts, other products related to paddle tennis may appear.
-
Phrase matching: We mark in inverted commas the part that must appear in the search, before and after other words may appear. Example: buy cheap "padel trousers".
-
Exact match: We determine the exact words with which we want our ads to appear. It is a way to be very relevant in the eyes of Google. We mark the exact words with square brackets, example: [paddle trousers].
In Google Ads there is also the possibility of choosing negative keywords. These are keywords for which we do not want to appear and can have any type of match: broad, phrase or exact.
How to get started with Google Ads?
If you are wondering how to get started with Google Ads, here are 5 steps to launch a campaign.
1. Create a Google Ads account
Go to ads.google.com and set up your Google Ads account. Select the type of account, enter your identification data, the name of your business... Once this first introductory step is done, we can start setting up the Google Ads campaign.
2. Create a campaign
The structure of a Google Ads account is made up of four types of elements: campaigns, ad groups, ads and keywords. Campaigns are the overall element, in which we will find the objective of one or more ad groups. One objective, one campaign.
On the other hand, the ad group is the internal structure of the campaign. These groups are formed by a list of keywords and the different ads.
Within a campaign we can configure: objective, campaign type, location, language, bidding strategy, daily budget and target audience.
The first requirement is to select which objective your campaign will have. Google Ads campaigns are very versatile, we can use them to target different phases of the conversion funnel. Here are the options:
-
Sales: Drive online sales.
-
Leads: Sales opportunities.
-
Website traffic: Getting more users to visit your website.
-
Brand awareness: This is a branding objective, to get more users to discover your product or service
There is also the option of creating a campaign without any of the above objectives.
3. Choose the type of campaign you want to use
Search Campaigns
Search Campaigns are text ads that are displayed in the top position when users search for a term on Google.
They are the recommended campaigns to increase sales, leads or website traffic.
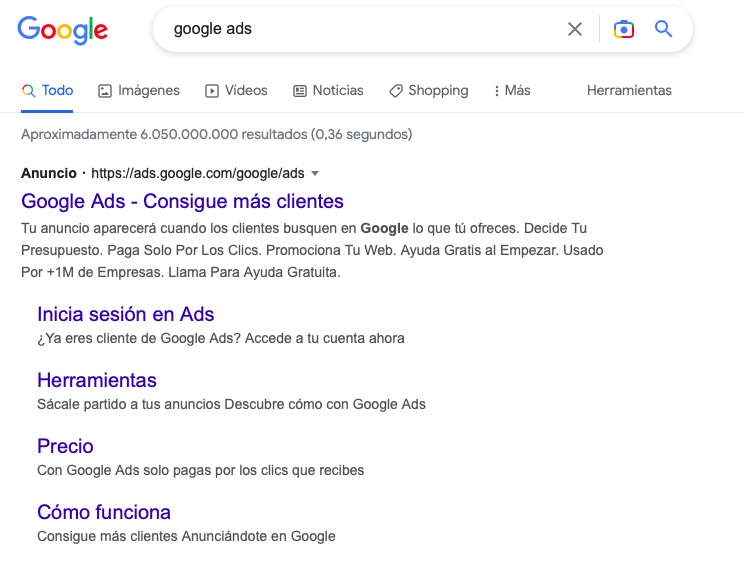
Performance Max Campaigns
Performance Max Campaigns are campaigns that reach audiences across all Google properties with a single campaign.
This solution optimises performance in real time and across all channels to achieve your goals.
Display Campaigns
Display Campaigns include images and text and are published on third-party sites that are part of Google's inventory of partner websites and locations.
With this campaign, you can expand your audience beyond the Google search engine.
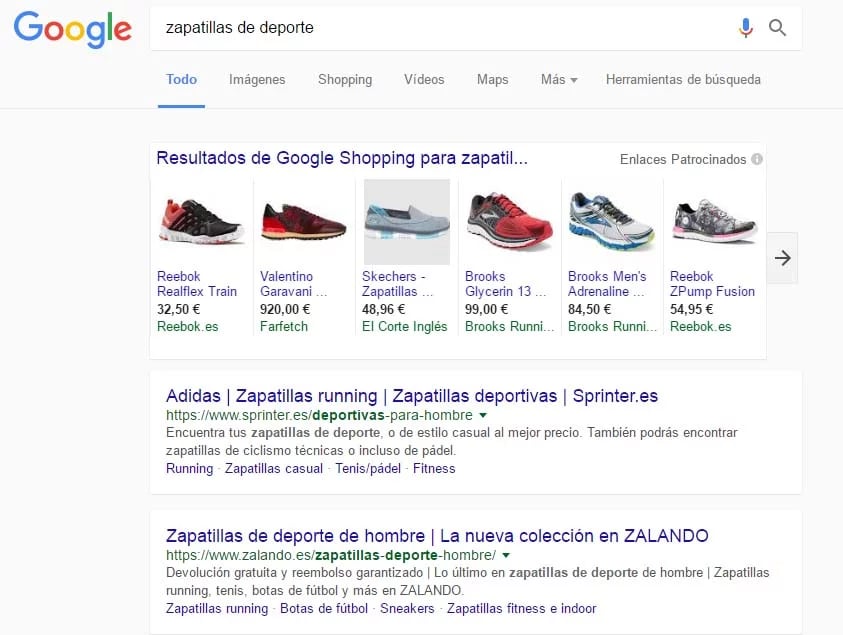
Shopping Campaigns
Shopping Campaigns are product cards that contain images and detailed information so that users can see the product features before clicking.
These types of campaigns are ideal for online shops.
Vídeo Campaigns
Video Campaigns are managed through YouTube Ads. There are three strategies for video campaigns:
TrueView
The True View format aims to engage and connect with users and drive sales. These ads can be found on YouTube display pages, web pages, social networks and Google Display Network applications. Depending on when they appear, there are 3 formats:
-
Pre-roll: the ad appears before the video. This is the most common advert and the one that captures the user's attention from the very first moment.
-
Mid-roll: the ad appears in the middle of the video. This ad is used in long videos as it functions as a pause to the content the user is watching.
-
Post-roll: the ad appears at the end of the video. It is recommended to redirect traffic to other pages.
Out-stream
Out-stream ads are used only on mobile devices and serve to extend the reach of video ads by appearing on Google's video partners.
Out-stream ads start playing without sound and the user can activate the sound by tapping on the video.
Bumper Ads
Bumper Ads have a maximum duration of six seconds and appear before, during or after another video and users do not have the option to skip this type of ad.
These ads are used when you want to reach a large audience with a short, memorable message.
Discovery Ads
This format allows for greater coverage on Google with a single ad campaign. In these ads, the video is displayed as a thumbnail on the homepage in search results or in related videos.
App Campaigns
App Campaigns allow you to promote Android and iOS apps through a search engine ad with the aim of generating downloads, leveling up or buying revenue or tools for the apps.
These campaigns are designed to get new users for the app and increase in-app sales.
Smart Campaigns
Smart Campaigns are a set of automated bidding strategies that employ machine learning and aim to increase conversions or improve conversion value.
Local Campaigns
Local Campaigns focus on growing offline business objectives. The goal of this type of campaign is to maximise the value of your shop through in-store visits, increase your offline sales and promote your locations through Google's inventory.
They streamline the process, making it easy to promote shops on Google's most prominent inventory: the Search Network, Maps, YouTube, Gmail and the Display Network.
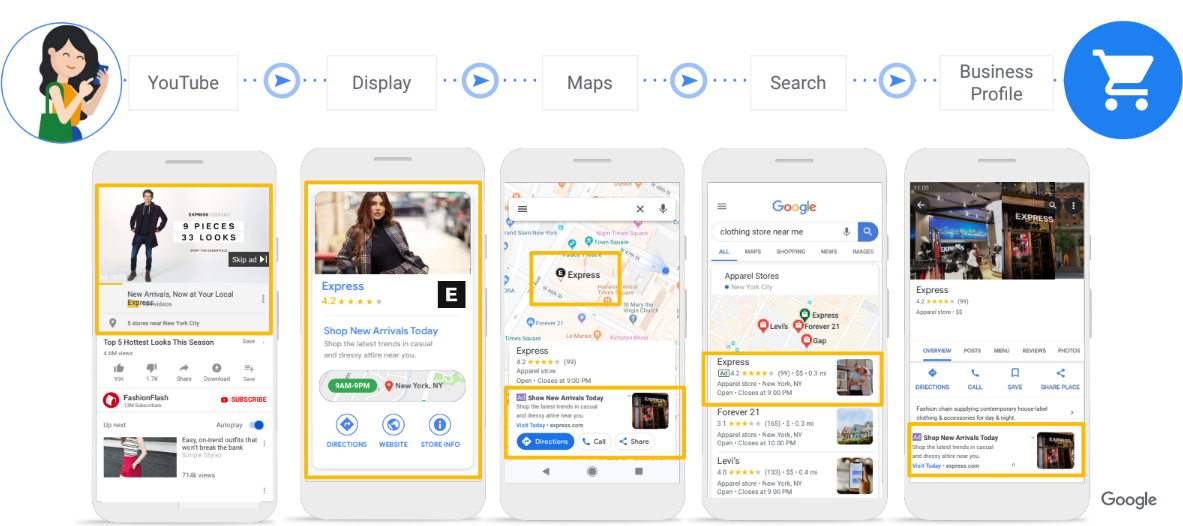
Discovery Campaigns
Discovery Campaigns enable your ads to reach over 3 billion customers across all feeds on the platform. Through audience signals and consumer intent, Google makes Discovery campaigns personalised, visual and engaging experiences for users.
Google Discovery Ads gives you access to YouTube, Discover feeds and Gmail's Promotions and Social tabs, allowing you to achieve greater reach with a single campaign.
Once you have selected the type of campaign, you need to decide how you want to reach the target: website visits, app download, phone call...
To finish creating the campaign we must name it and select the networks where we want the ads to be shown (always taking into account the type of campaign we are creating). There are two options:
-
Search Network: Ads will appear in search results, on other Google sites (such as Maps, Shopping or Google Images) and on Google search partner websites. These partners can be selected or ignored as preferred. As long as the user searches for terms relevant to your keywords.
-
Display Network: Ads will be shown to relevant customers when they visit a website, play a video or use an app. This is a way to extend the reach of your ads, as Display Network sites reach over 90% of internet users.
Before you start setting up your ad groups, don't forget to: define the target audience, the browser language and the location where your ads will be shown. It is also time to define how much you want to spend (budget) and how you want to spend it (bid). The budget will mark the average daily amount that we will invest.
4. Set up the ad group
Once the campaign is set up, we need to create the ad group. These contain one or more ads and a set of keywords related to the product or service that each ad group will promote.
In this step we must select: the name of the ad group, the determined bid and the keywords. To control the searches that will trigger our ads, we must select in this step the type of match we want to use with each keyword.
2 TIPS: Don't forget negative keywords and to include the name of your website as a keyword if your competitors are bidding for your brand or you are not ranking for it organically.
Good keyword research can make all the difference to the success of your ads. What should we look at to determine whether a keyword is of interest to us or not?
-
Search volume
-
Competition and price per click
-
Intent
Once all of these are configured and based on the bid and budget, Google will show us an estimate of traffic.
5. Create ads within the ad group
The structure of a Google ad includes: landing page URL, 3 titles or headlines and 2 descriptions. This type of ad is known as ETA (Expanded Text Ads) and will disappear on 30 June 2022.
There are also responsive search ads, which allow up to 15 titles and 4 descriptions.
The ideal formula? 2 ETAs and 1 responsive ad.
In addition to these basic elements, there are additional elements that your ad should contain depending on the type of campaign you have set up.
-
For Display Network: Several images adapted to Google regulations (size and weight).
-
For Shopping: Have a product feed ready to upload to Google Merchant Center, Google's tool for managing catalogues.
-
For Video: Content in video format.
TIP: In a maximum of 80 characters, the description should: address a need of the target, show a value to buyers, present an offer to influence the buying process or an ideal solution.
Once the ad is set up, we can include up to two more options within the ad group. Based on the performance of each, Google will display the one that works best.
You can also experiment with other key elements such as calls to action, visible URL, landing page... and do an A/B test. For this to work and be effective, we must wait until both versions of an ad have received a significant number of impressions and clicks to allow us to draw conclusions.
With the ads created, it's time to publish your Google Ads campaign!


![[Ebook] SEO + AI: eBook to Master AI Overviews and GEO](https://www.adsmurai.com/hubfs/MKT%20-%202025/WEB/Resources%20-%20Banners/HeaderEN_Ebook_SEO+AI.png)


